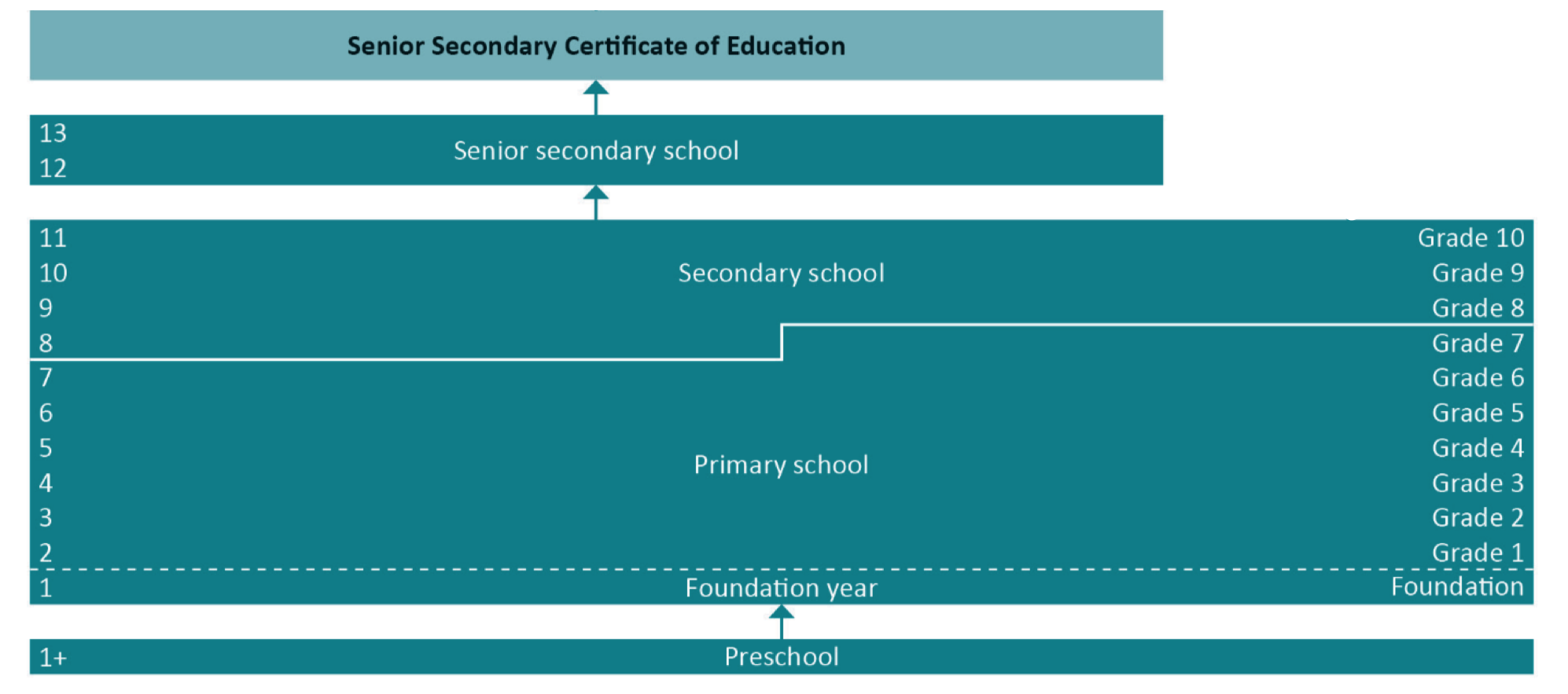
School education is compulsory in Australia. Children must start going to school no later than 6 years of age. However, most children start earlier, at the age of 4-5. The Australian school system varies slightly from state to state. For example, in the Australian Capital Territory and New South Wales, kindergarten is part of a primary school, while in the rest of the states, it is considered preschool education. In some states, primary school ends at Year 6, and at Year 7 in others. But, in general, the school education system in Australia can be divided into:
- Primary school – from year 0 to 6 (or 7 in a few states).
- Secondary school – from year 7 (or 8) to 10.
- Senior secondary school – years 11 and 12.
Primary school
Children go to primary school from the age of 5-6 and finish it by the age of 12-13. At primary schools, there is an emphasis on developing literacy, numeracy and social skills. The core subjects are English reading and writing, maths and the Study of Society and the Environment (SOSE). Children also study music, art, computing, science, and a foreign language. Students can also take part in numerous extracurricular activities such as sport, choir, orchestra, theatre, etc.
Secondary school
Secondary school level lasts from years 7-8 to year 10. The main study areas are English, human society and its environment, languages, mathematics, personal development, health and physical education, science, creative arts and technology. Subjects in these areas are compulsory, but students also have an opportunity to choose electives. At this stage, children try a variety of spheres to understand their inclinations and future specialisation.
After year 10, students can leave the school and continue their education at VET courses or go to work. However, in order to enter a higher education institution, they must complete years 11 and 12.
Senior secondary school (high school)
The high school curriculum is more specialised. Students continue to study English as a core subject and a few other elective subjects (at least three). Most students choose subjects for university preparation, focusing on areas they want to study at universities, such as maths and science, arts, humanities or business.
At the end of year 12, students pass exams and receive a certificate of secondary education completion. Every state has its own name for this certificate, but all of them are recognised by Australian tertiary education providers.

Types of schools in Australia
Mandatory schools in Australia can be divided into government (public/state) and non-government such as Catholic or a number of private schools. About 70 per cent of Australian children prefer public schools.
Apart from mandatory schools, Australia has many cultural and religious schools or schools based on any educational philosophy (for instance, Montessori or Waldorf-Steiner).
Most of the schools are co-educational, but some teach only boys or only girls. There are also boarding schools where children live in an environment that helps develop their talents and interests. Such schools often have a part-time boarding option where students can go home on weekends.
Selective schools are schools for talented students. They accept children with outstanding academic achievements. Specialist schools offer programs focused on a particular sphere like arts, sports, science, etc. To enrol on these schools, students should pass exams and are usually very competitive.
School facilities
Australian schools are considered to be among the best in the world. Facilities and equipment are always modern and extensive. Digital interactive whiteboards in classrooms, computer labs, wireless computer networks, libraries and science labs can be found in every Australian school. Apart from classes, children participate in extracurricular events such as concerts, theatre plays and excursions. For these purposes, schools also have music rooms and musical instruments, theatres or concert halls.
Great attention is paid to sports. Schools always provide excellent sporting facilities such as various sports grounds, courts, swimming pools and gyms.
In most Australian schools, children have to wear a uniform. Each school has its own uniform design in the school colours.
For a comfortable learning environment and individual approach to children, the number of students in a class is limited to 30.
If your child doesn’t speak English well, it is not an issue. Schools have special teachers who run classes on English as a foreign language for international students. As a rule, children adapt quickly to the new language and start speaking English very quickly.
The school must report on the child’s progress at least twice a year. The report is submitted to parents in written form and includes results in every subject, a record of other activities and comments on behaviour, personal development and attendance. There is also an opportunity to meet every teacher at least twice a year. Meetings are always private and last for around 10 minutes.
School Term Dates
The academic year starts at the end of January / beginning of February. It is divided into four terms of approximately 10 weeks with holidays between them. Holidays usually last two weeks, but from mid-December to late January, schoolchildren have a long Christmas break. The exact dates for starting school studies and holidays may vary from state to state. Thus, In the Northern Territory, the school year begins in January, and children have four-week holidays in the middle of the year when the weather is drier and cooler. In non-government schools, the schedule may differ from public schools.

Accommodation
If an international student comes to Australia without parents, there are two accommodation options for them:
Homestay. An option when a student stays with an Australian family. A student is treated as a family member. It helps in adapting and practising English. All the families are reliable as they are regularly checked by police and the school. Homestay fee includes an individual furnished room, internet access and three meals a day.
Boarding. This option is available in non-government schools that have dormitories. Children usually share a room with a few other students, but in years 11-12, they can live in a single room. In dormitories, children are always under the supervision of qualified staff responsible for their safety and well-being.
Fees
If a child has domestic student status, they can attend public school for free. The school can charge some voluntary fees, but they are not compulsory. International students have to pay tuition fees in full, whether it is a government or non-government school. Private schools can cost up to AUD $35,000 per year. In public schools, the tuition fee for international students can vary from AUD $13,500 – $17,000 per year (depending on the year). Some additional costs may also occur:
- uniforms AUD $250-300
- Insurance AUD $600 for 12 months
- School books and equipment
- Excursions and other activities
It is worth mentioning that dependent children of international students usually have discounts for public school tuition fees. For them, the price can vary from AUD $6,300 to $13,000 depending on the year, the state, and the parent’s visa. Please, read our article about coming to Australia with children.

Enrolment Process
The main feature of Australian government schools is that each school serves a specific territory (area) and accepts children who live in this school area. Thus, if you want your child to go to a particular school, you need to look for housing in its area. When enrolling, you will need to provide proof of address. If you want to register a child in a school from another area, the child can be accepted on an individual basis and only if there are vacancies.
Independent schools accept all the students irrespective of their living areas. However, it is recommended to contact a private school for the enrolment as early as possible because there can be long waiting lists. In some prestigious schools, the competition is so high that many parents put their children on a waiting list at birth.
Documents required for the enrolment
When enrolling in a public school, you will have to provide a child’s passport or birth certificate, visa and proof of address. Additionally, it is recommended to provide the following information:
- The year/class the child was at in their previous school;
- Information about immunisation;
- Other important medical information (allergies, chronic diseases, etc.);
- Any special programs the child has been in (for example, English as a Second Language).
Independent, selective and specialist schools may have their own requirements as well as entrance exams and proof of a child’s previous academic or sports achievements. Therefore, check the entry criteria of each private school on their website.
Schools in Australia are aimed not only at providing knowledge, but also at the comprehensive development of children, such as their personal, creative and sporting potential, and leadership qualities. All this is combined with a safe and friendly environment and excellent facilities. Your child will enjoy going to school in Australia.



